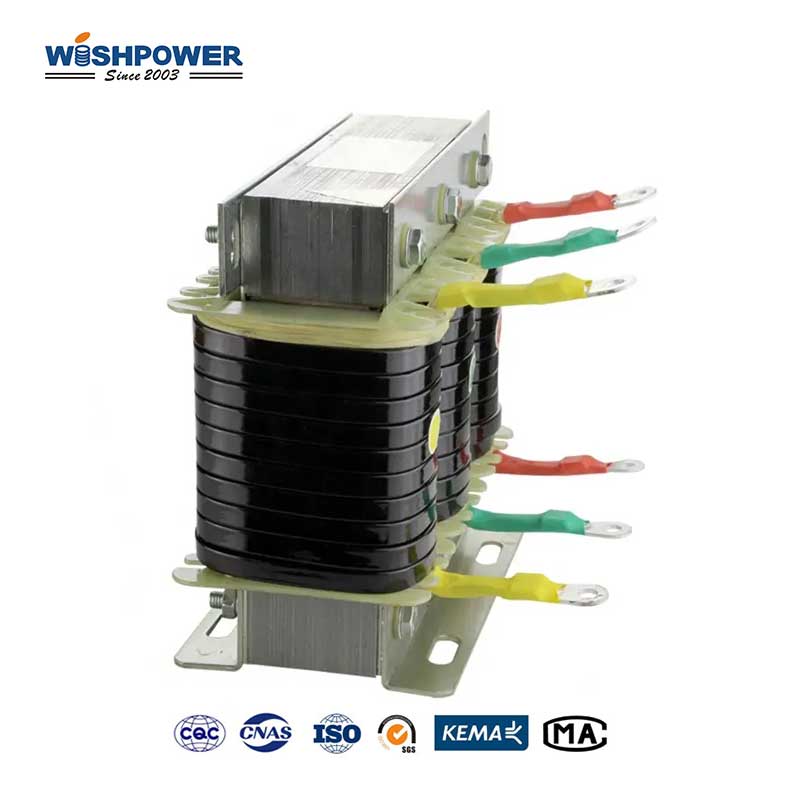
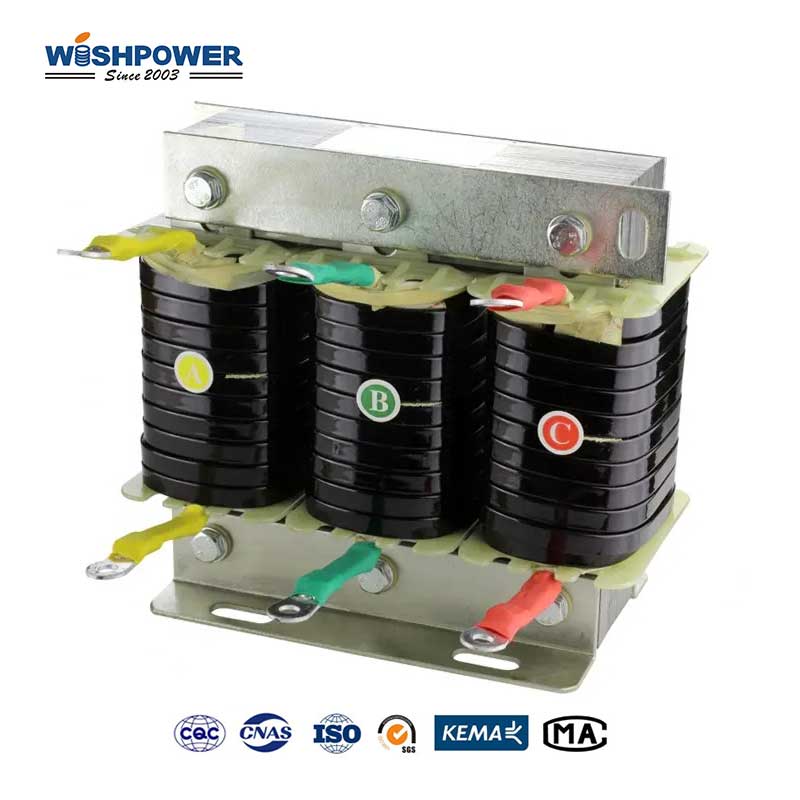
Specification
|
Standard
|
EN60076-6, EN 61558-2-20
|
Rated Voltage
|
230V to 690V
|
|
Dielectric test
|
50HZ 3KV ,60s
|
Rated Frequency
|
50HZ/60HZ
|
|
Cooling method
|
natural air
|
Certification
|
CE, TUV
|
|
Ambient temperature
|
-25 to +50 ℃
|
Elevation above seal level
|
≤2000m a.s.l
|
|
protection Class
|
IP00 indoor mounting
|
Inductance tolerance
|
0±5%
|
|
Blocking factor
|
5%—14%
|
Linearity
|
1.55–2.2ln
|
|
Insulation Class
|
H
|
Max humidity
|
95%
|
|
Winding material
|
Copper/ Aluminum
|
Thermal protection
|
135℃ normally closed switch
|
The table above is just one of our product parameters. If you want more information, please get in touch with info@wishpower.net
What is the Dry Type High Voltage Shunt Reactors?
The high-voltage dry-type shunt reactor is a reactive power-absorbing electrical device that is used to regulate the voltage levels of a high-voltage power system. Shunt reactors are connected in parallel with the system and specifically engineered to offset the reactive power of long transmission lines or underground cables and the capacitive reactive power thus generated. They absorb excess reactive power, which prevents overvoltages, increases voltage stability/efficiency of the power network, and protect and depressurize insulators by acting as a current balancing device. These reactors don’t use oil or other liquid insulation, but only air or solid insulation materials instead; therefore, they are called “dry type.” They are safer, and more environmentally friendly because they reduce the risk of leaks or fires. This application is sometimes used in substations or directly in power lines for improved voltage control and prevention of deterioration caused by voltage instability, especially in lightly loaded or long-distance power lines.
Market Trends
Growth in the shunt reactor market has been growing steadily because of the demand for reliable voltage regulation and power quality in modern electrical grids. With the increasing amount of renewable energy sources like wind and solar power, a surprisingly vital component of power systems, voltage stabilization, which proves to be efficient for both economic and technical reasons is required when reactive power may fluctuate constantly. In systems where long-distance transmission lines or underground cables predominate, these reactors are vital to ensure grid stability considering that excess reactive power from such systems has to be controlled. The growth of this market has also benefited from advancements in insulation materials and cooling systems, which have resulted in more efficient, compact, and environmentally friendly insulation for insulation insulation insulation insulation. The lack of liquid insulation lowers the risk of fire and environmental hazards, which are excellent choices in strict environmental zones.
Differences compared to transformers
Although both are inductive components, the fixed shunt reactor, and the transformer have unique responsibilities to perform within electrical power systems. The key distinction lies in their purposes: A shunt reactor is principally designed to absorb reactive power in a power grid and to control voltages while a transformer is used to transfer electrical energy between different voltage levels (of course stepping up or down the voltage for the best transmission and distribution). A reactor works to nullify the capacitive effects in the transmission lines or cables at the end of an electrical line; a transformer performs its involvement to adapt the varying distance and load to allow power transmission to take place. The reactive power management is not something that transformers generally do, and shunt reactors are designed for that very reason.
Precautions
- Proper Ventilation:
The shunt reactor in substation depends on air for cooling, so make sure it gets enough air around it to prevent overheating.
- Correct Voltage Rating:
Never use a reactor having a voltage rating of the specific power system but is not suitable so that no overvoltage or undervoltage may occur.
- Regular Insulation Checks:
Check periodically over the insulation for signs of wear or damage to prevent electrical fault or failure.
- Avoid Overloading:
You don’t want to overload the reactor, because if you do it can cause poor efficiency, overheating, and even physical damage.
- Monitor Operating Conditions:
Monitor all environmental conditions continuously to ensure that the reactor is within its advertised limits for safe and dependable performance.
Certificate

Factory

Hot Tags: Dry Type High Voltage Shunt Reactors, Reactor, Thailand, manufacturers, ISO factory, wholesale, KEMA, high quantity, best, price, low to high voltage




















